Understanding the Procedure of Hysterectomy: An In-Depth Guide
Hysterectomy is a significant surgical procedure often recommended for various medical conditions related to the female reproductive system. As an essential topic within the fields of health and medicine, this article provides a comprehensive examination of the procedure of hysterectomy, including its types, benefits, potential risks, and post-operative care. Whether you are considering this procedure or simply seeking more information, our detailed guide is here to help.
What is Hysterectomy?
A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. In some cases, other reproductive structures may also be removed, including the cervix, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. This procedure is often recommended for women experiencing severe gynecological issues such as:
- Uterine fibroids: Noncancerous growths that can cause pain and heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: A painful condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside of it.
- Uterine prolapse: A condition where the uterus slips from its normal position into the vaginal canal.
- Chronic pelvic pain: Persistent pain in the lower abdomen that can be caused by various conditions.
- Abnormal bleeding: Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding that isn't resolved by other treatments.
Types of Hysterectomy Procedures
There are several different types of hysterectomy procedures, and understanding each can help patients make informed decisions regarding their health:
1. Total Hysterectomy
A total hysterectomy involves the removal of the uterus along with the cervix. This is one of the most common forms of hysterectomy.
2. Subtotal (Partial) Hysterectomy
A subtotal or partial hysterectomy is when the uterus is removed but the cervix is left intact. This option may be suitable for certain conditions.
3. Radical Hysterectomy
A radical hysterectomy is a more extensive procedure typically performed when cancer is present. It involves the removal of the uterus, cervix, surrounding tissues, and sometimes the upper part of the vagina.
4. Hysteroscopic Hysterectomy
This minimally invasive procedure allows for the removal of the uterus through the vagina using a hysteroscope. It is mostly used for smaller fibroids or abnormal growths.
Preparing for a Hysterectomy
Preparation for a hysterectomy involves several crucial steps to ensure optimal outcomes:
- Consultation with a Specialist: Patients should discuss their symptoms, medical history, and treatment options with their healthcare provider.
- Pre-operative Testing: Blood tests, imaging scans, and other evaluations are often required.
- Medication Review: Any medications taken, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, must be reviewed.
- Understanding the Procedure: Patients should be informed about the specific type of hysterectomy they will undergo and what to expect.
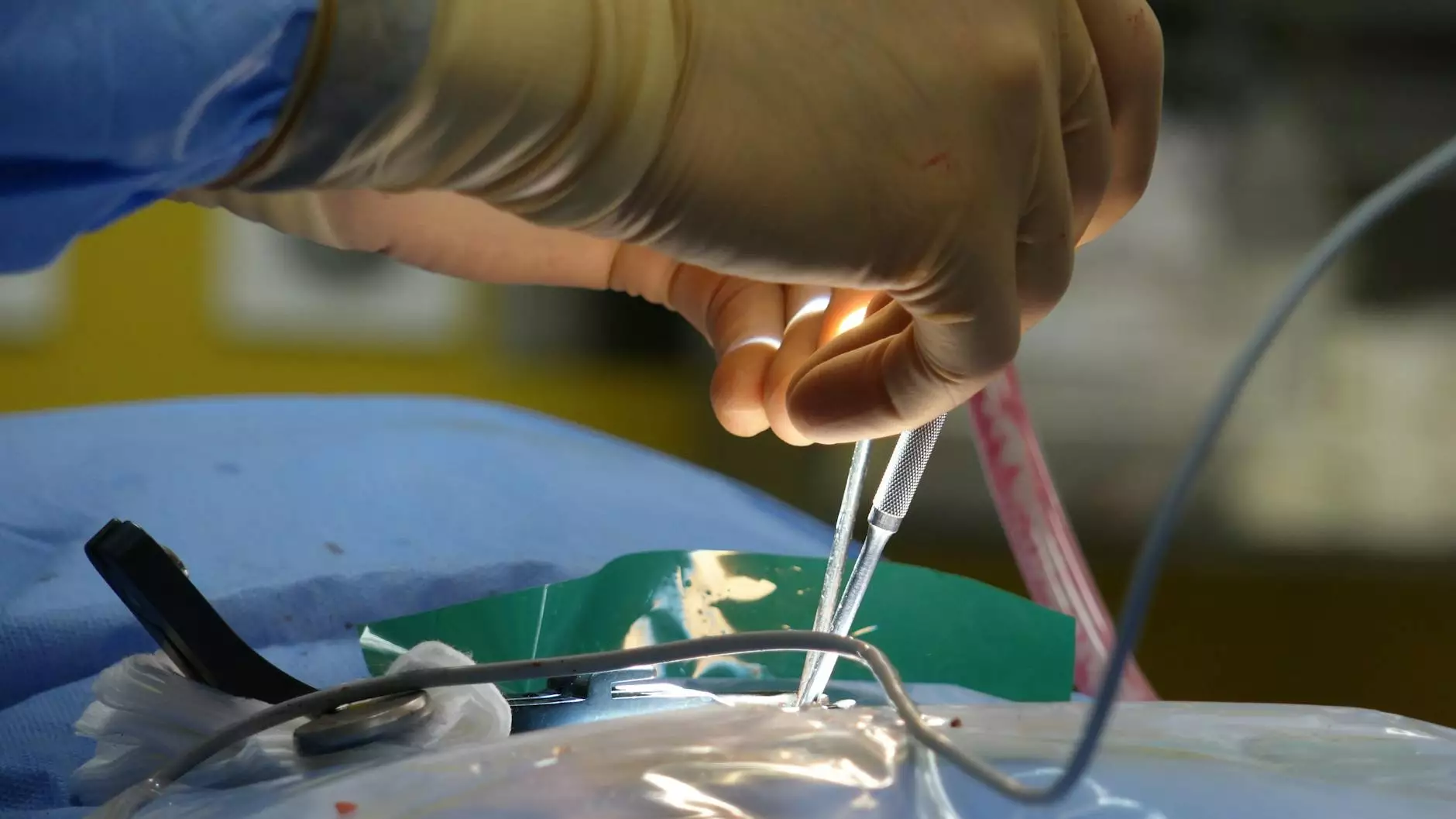
The Hysterectomy Procedure
The actual procedure of hysterectomy can vary based on the type chosen and the patient's medical condition. However, here is a general outline of the procedure:
1. Anesthesia
Before the surgery begins, the patient is given anesthesia. This may be general anesthesia (where the patient is fully asleep) or regional anesthesia (where the lower body is numbed).
2. Surgical Incision
The surgeon will make an incision in the abdomen or perform the surgery via the vagina, depending on the approach:
- Abdominal Hysterectomy: The incision is made in the lower abdomen.
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Small incisions are made in the abdomen, and the uterus is removed with the aid of a camera.
- Vaginal Hysterectomy: The uterus is removed through the vaginal canal.
3. Removal of the Uterus
Once the proper incision is made, the surgeon carefully removes the uterus. If necessary, other reproductive organs may also be removed.
4. Closing the Incision
After the removal is complete, the surgeon will close the incisions using stitches, surgical glue, or staples, depending on the surgical method used.
Benefits of Hysterectomy
While the decision to undergo a hysterectomy is significant, the benefits can be profound, particularly for women suffering from chronic gynecological problems. Some benefits include:
- Pain Relief: Many women find significant relief from chronic pelvic pain following a hysterectomy.
- Elimination of Heavy Bleeding: For those suffering from heavy menstrual bleeding, a hysterectomy can resolve this issue completely.
- Improved Quality of Life: Many women report an overall enhancement in their quality of life, allowing them to return to normal daily activities.
- Reduction in Cancer Risk: In cases where the surgery is performed to remove cancerous growths, a hysterectomy can significantly reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with a hysterectomy. Some potential complications include:
- Infection: Surgical site infections can occur, requiring further treatment.
- Excessive Bleeding: Some patients may experience heavier bleeding than normal during or after the surgery.
- Blood Clots: There is a risk of developing blood clots in the legs or lungs following surgery.
- Damage to Surrounding Organs: There is a small risk of damage to nearby organs, such as the bladder or intestines.
- Emotional Impact: Some women may experience emotional challenges, including feelings of loss or changes in body image.
Post-operative Care and Recovery
Recovery following a hysterectomy varies based on the type of procedure and individual health factors. Here are key points on post-operative care:
1. Hospital Stay
Patients may stay in the hospital for one to three days depending on the type of surgery performed. During this time, medical staff monitor for any complications.
2. Pain Management
Pain relief medications are often prescribed to help manage post-operative discomfort. It's essential for patients to communicate openly about their pain levels.
3. Activity Restrictions
Patients are usually advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for several weeks post-surgery. Gentle walking is encouraged to aid in recovery.
4. Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring recovery and addressing any concerns.
Emotional Support and Counseling
It's normal for women to experience a range of emotions after undergoing a hysterectomy. Feelings of sadness, relief, or even grief are common, especially if the surgery is linked to fertility issues. Seeking emotional support through counseling or support groups can be beneficial for many women.
Conclusion
The procedure of hysterectomy is a life-changing decision that can bring relief from debilitating symptoms and improve quality of life for many women. Understanding the types of hysterectomies, preparation steps, benefits, risks, and recovery process can empower patients to make informed choices about their health. If you are considering a hysterectomy or want more information, reach out to a qualified healthcare provider who can guide you through this important journey.
For expert insights and personalized care, visit Dr. Seckin, where comprehensive gynecological services are provided with compassion and expertise.